Personal safety guidelines in workshops must keep in mind
Safety

Safety in a workshop can be broadly classified into 3 categories :
General safety
Personal safety
Machine safety
Personal Safety:
Wear a secured boiler suit; avoid loose clothing, jewelry, and accessories.
Use safety footwear; keep hair short.
Never lean on machines or clean hands with coolant fluid.
Start machines only after securing workplaces and ensuring a clear area.
Avoid distractions and faulty electrical equipment; only authorized electricians should handle connections.
Safety

Occupational safety and health Tips:
1. Be aware of your surroundings.
2. Maintain a correct posture Take break regularly.
3. Use Equipment properly.
4. Locate Emergency Exits.
5. Report Unsafe conditions.
6. Practice Effective Housekeeping.
7. Make use of mechanical aids.
8. Wear the correct Safety equipment Reduce workplace stress.
Safety
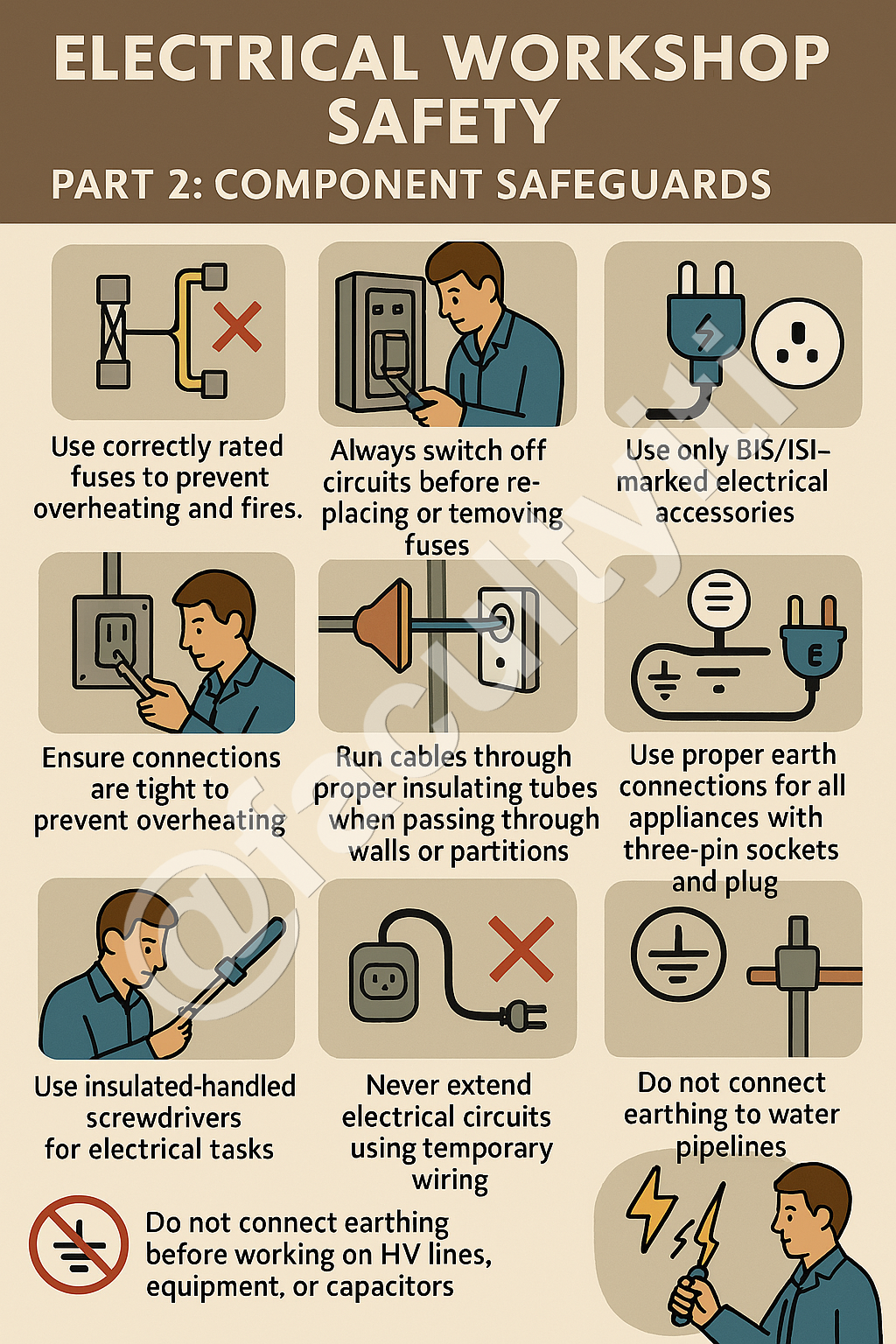
Electrical Workshop Safety
Part 2: Component Safeguards
1. Use correctly rated fuses to prevent overheating and fires.
2. Always switch off circuits before replacing or removing fuses.
3. Ensure connections are tight to prevent overheating.
4. Use only BIS/ISI-marked electrical accessories.
5. Run cables through proper insulating tubes when passing through walls or partitions.
6. Use proper earth connections for all electrical appliances with three-pin sockets and plugs.
7. Never extend electrical circuits using temporary wiring.
8. Do not connect earthing to water pipelines.
9. Discharge static voltage before working on HV lines, equipment, or capacitors.
10. Use insulated-handled screwdrivers for electrical tasks.
Safety

Electrical Workshop Safety
Part 3: Fire & Accident Prevention
1. Always use lamp guards for extension cords to avoid bulb breakage and fire risks.
2. Place hot soldering irons in stands—never on workbenches.
3. Display “Men on Line” signs when working on dead circuits.
4. Remove fuse grips for safety when working on circuits.
5. Ensure accessories (sockets, plugs, switches) are in good condition.
6. Stand on rubber mats when operating switch panels or control gears.
7. Identify proper machine operation before use.
Keep combustible materials away from electrical heat sources.
Safety

Electrical Workshop Safety
Part 1: Personal Safeguards
1. Only qualified individuals should perform electrical work.
2. Keep the workshop clean and tools in good condition.
3. Avoid working on live circuits; if necessary, use rubber gloves, mats, and insulated tools.
4. Never touch bare conductors.
5. Stand on a wooden stool or an insulated ladder when handling live circuits.
6. Position ladders on firm ground and have a helper hold them.
7. Wear a safety belt when working on poles or elevated points.
8. Avoid loose clothing near rotating machinery.
9. Never interfere with machine interlocks.
10. Do not use water on electrical equipment.
Clutch

Types of Clutch Linings:
1. Solid Woven Lining types
2. Moulded Lining types
Solid Woven lining type In this type, Clothes are stitched with the suitable thickness.
Moulded lining types It is formed with the help of asbestos, fibre, glass particles, cloth, metal powder and sticking component with particular pressure.
Clutch
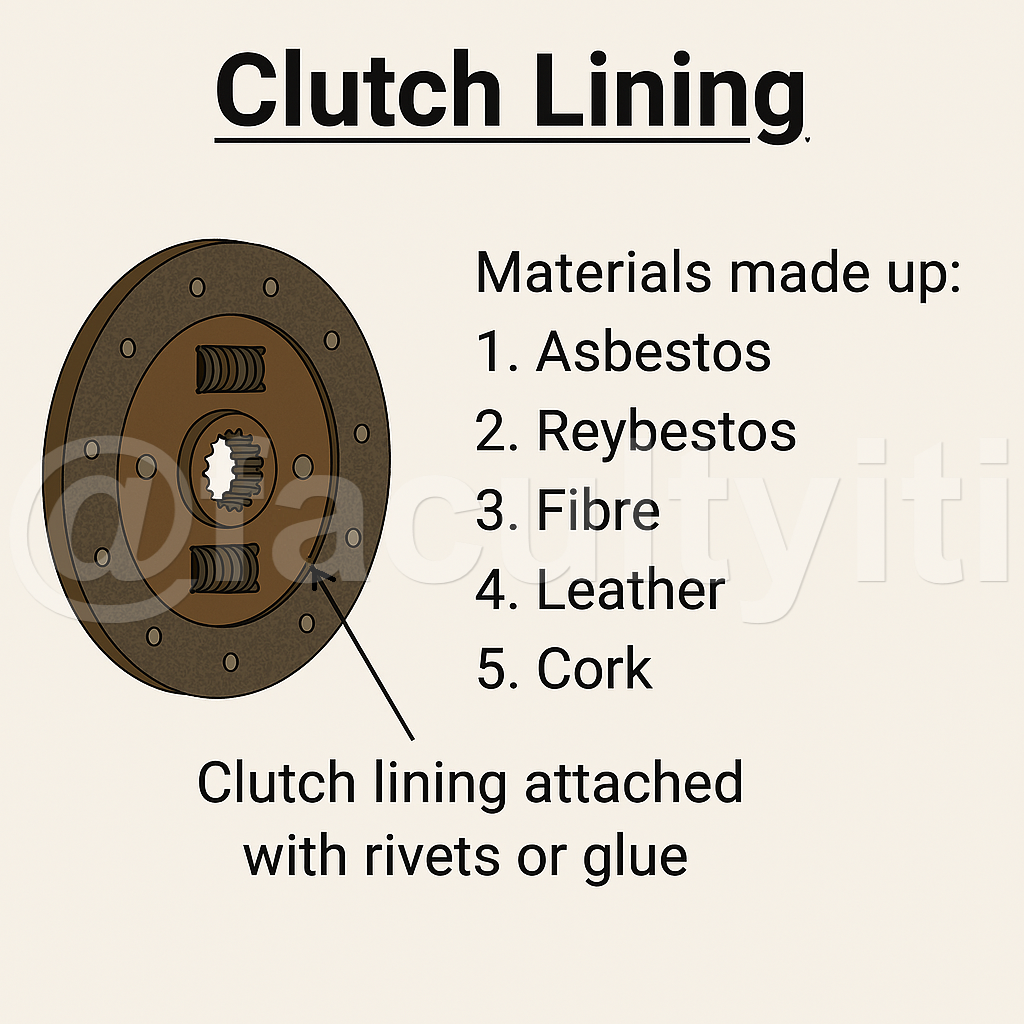
Clutch Lining The two ends of the clutch lining and clutch plate are attached with the help of rivets or some special glue.
The clutch lining is made up of following materials.
1. Asbestos
2. Reybestos
3. Fibre
4. Leather
5. Cork
Clutch

The clutch plate is made of steel with a centrally located hub containing splines. It has moving capacity and is attached to a disk surrounded by cushion springs. Friction lining is secured with rivets or glue. A helical spring in the center absorbs torque, known as the torsional or damper spring.
Clutch

Components of Clutch :
1. Clutch Plate
2. Clutch Lining
3. Pressure Plate
4. Coil Spring
5. Release bearing
6. Clutch linkage
Clutch

Qualities of Good Clutch :
1. Should have high torque transmission.
2. Should join in step-by-step.
3. Should be a good transfer of heat.
4. Operating balance is required.
5. Should be able to bear the shocks.
6. Should have free pedal play.
7. Should be easy to operate.
8. Should be in simple construction, cheap in cost and high working life.
9. Low space should be adequate.
10. Should have high co-efficient of friction
Introduction to Automobile

Electrical system supplies electrical energy which is used to produce the spark for igniting the air fuel mixture in petrol engines, to provide light for the vehicle during night ride, to operate the wiper motor, to light inside the vehicle, to play music and for dashboard lights.
Introduction to Automobile

Wheels and Tyres: The wheels help to carry the vehicle’s entire weight and to drive the vehicle. The wheels are connected to the front and rear axles of a vehicle. They absorb the vibrations produced from the road and help to keep the tyres soft and smooth
Introduction to Automobile

Brakes are installed on the four wheels of the vehicle and work through mechanical connections, hydraulic and air. The very important part of an automobile is the braking system that helps to drive and control the speed of the vehicle within safe speed.
Introduction to Automobile

The steering system operates on a very simple mechanism that directly transforms steering wheel rotation into straight line movement and helps in turn the vehicle as per the road.
Introduction to Automobile

Suspension System is the Spring Shock absorber has been connected to the front and back axles and helps to drive the vehicle smooth and slower from the vibrations in the road.